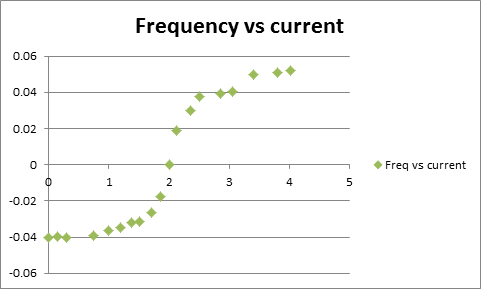
Experiment 1
Method used: Henry’s method and PASCO sensor
Needle used: 5.35cm long, 100 loops of wire
In this experiment, the needle was magnetized by following process:
- Disconnect the wire wrapped around the needle, turn the current to zero;
- Connect the power supply with the wire;
- Gradually increase the current to desired value;
- Decrease the current till 0;
- Disconnect the wire and measure the magnetic strength of the needle;
- Reverse the current direction, repeat the above procedure.
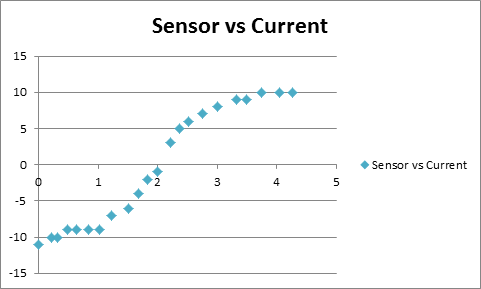
The amplitude and direction of current used to magnetize the needle and the deflection angle of the compass were recorded. The result is shown in the following graph:
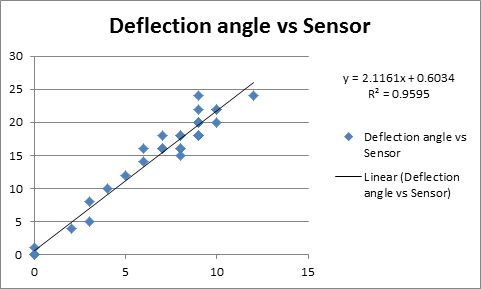
Experiment 2
Method used: Henry’s method and PASCO sensor
Needle used: 5.35cm long, 100 loops of wire
In this experiment, the needle was magnetized by following process:
- Disconnect the wire wrapped around the needle, turn the current to zero;
- Connect the power supply with the wire;
- Gradually increase the current to desired value;
- Decrease the current till 0;
- Disconnect the wire and measure the magnetic strength of the needle;
Part 1) Negative current
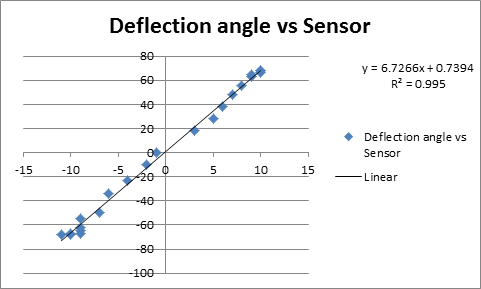
In this part, the needle was magnetized by a large positive current (>4A) to achieve max magnetization (11 Gauss) first and then magnetize the needle using increasing negative current to get different magnetic strength. Results are shown in the following graphs:
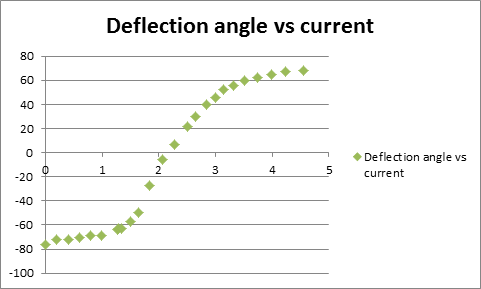
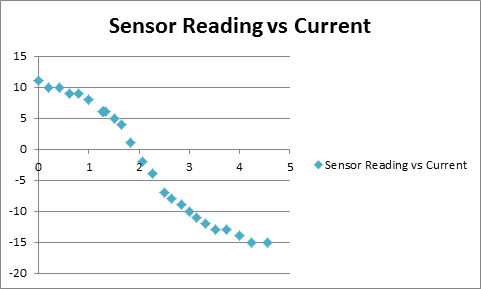

Part 2) Positive current
In this part, the needle was magnetized by a large negative current (>4.5A) to achieve max magnetization (-11 Gauss) first and then magnetize the needle using increasing positive current to get different magnetic strength. Results are shown in the following graphs:

Experiment 3
Method used: Savary’s method
Needle used: 5.35cm long, 100 loops of wire, needle is placed about 5cm above the magnet.
In this experiment, the needle was magnetized by following process:
- Disconnect the wire wrapped around the needle, turn the current to zero;
- Connect the power supply with the wire;
- Gradually increase the current to desired value;
- Decrease the current till 0;
- Disconnect the wire and measure the magnetic strength of the needle.
After each time of magnetization, the needle was made to oscillate and the time used for 30 oscillation was recorded. Following is the plot of the inverse of 30 periods vs. current: