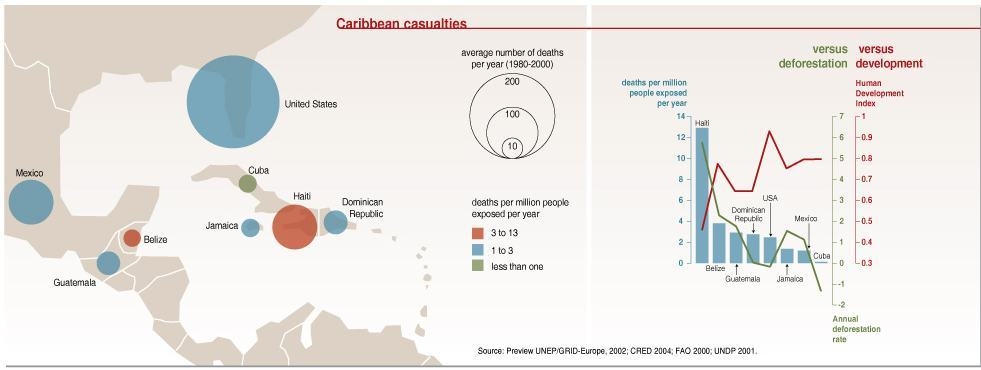
Caption
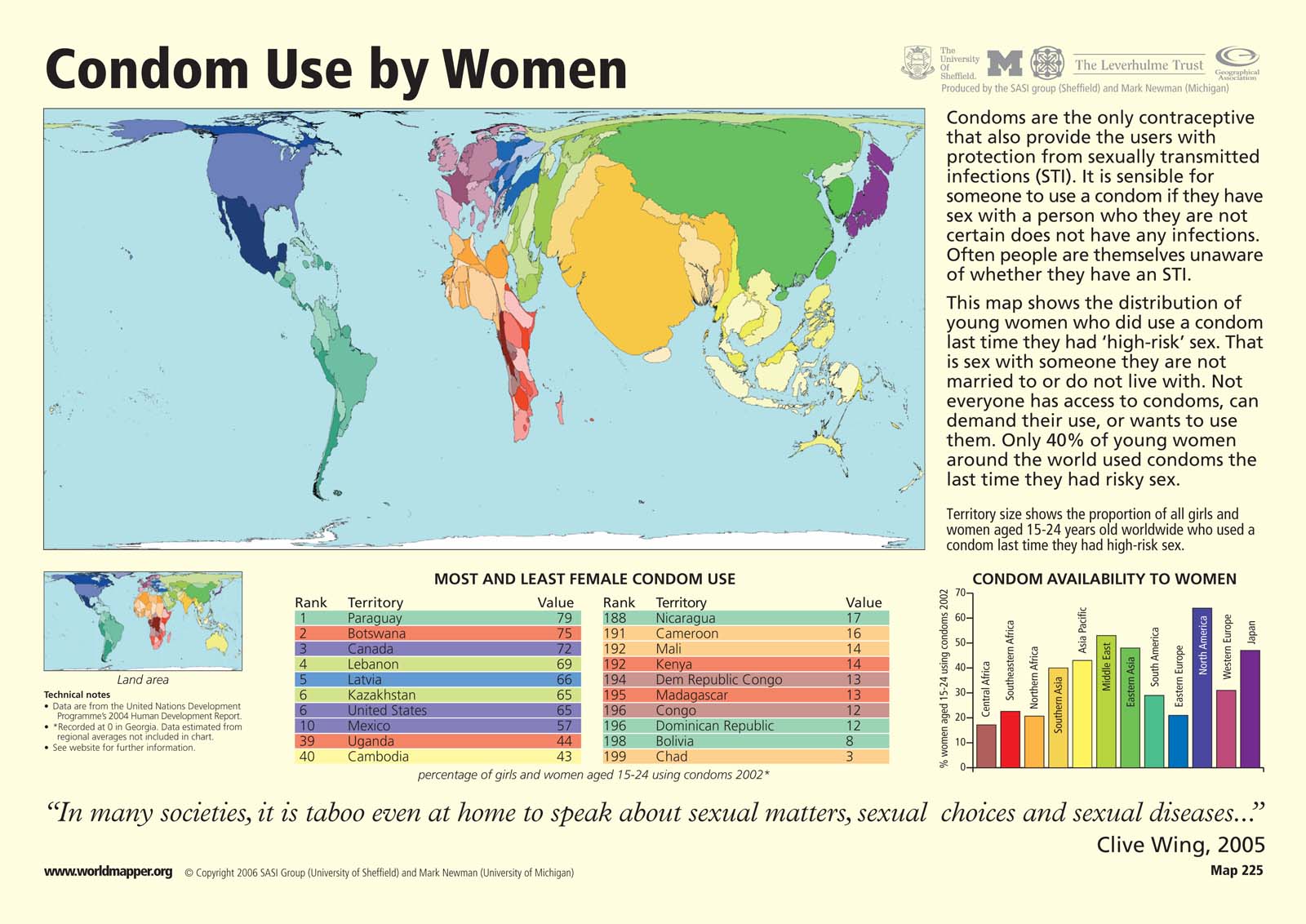
Condom Use by Women
Summary
This “Worldmapper” map shows condom use by females aged 15-24 by country. Territory size shows the proportion of all females aged 15-24 worldwide who used a condom the last time they had high-risk sex. High-risk sex is defined as sex with someone that the woman is neither living with nor married to. Country size does not take population into account. Therefore, countries like the United States with high condom use per capita may be shown smaller on the map than countries like India, with a lower level of condom use per capita but a larger total population.
The map is accompanied by two tables that show ranked lists of the ten countries with the highest and lowest percentages of females using condoms in 2002. There is also a bar graph that shows the percentage of females aged 15-24 using condoms by region.
Copyright status
© Copyright 2006 SASI Group (University of Sheffield) and Mark Newman (University of Michigan)
Used on QED by permission.
Licensing
All rights reserved
































,_1953.jpg)